Groundbreaking New Technique Unveils Early Earthquake Signs
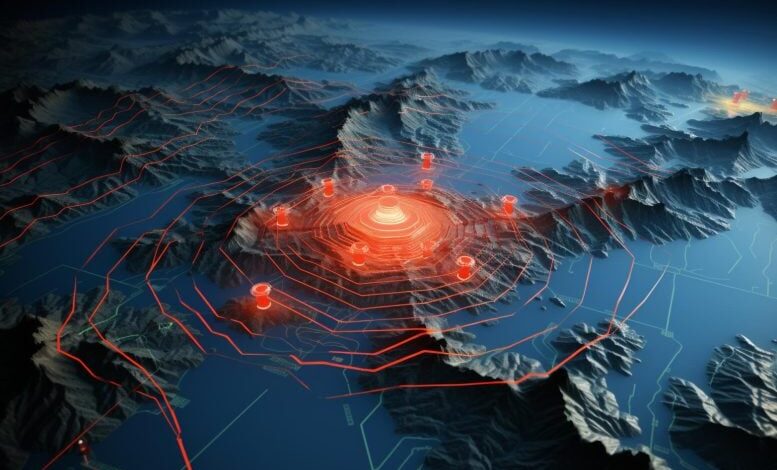
A new study highlights the potential of satellites in detecting early indicators of earthquakes through anomalies in the ground, atmosphere, and ionosphere, suggesting the possibility of predicting earthquakes earlier than previously thought. Professor Mehdi Akhoondzadeh’s research, which involved analyzing satellite data from recent earthquakes near the Turkey-Syria border, identified significant precursor anomalies occurring up to 19 days before the events. These findings could pave the way for developing advanced earthquake early warning systems that minimize false alarms and increase prediction reliability. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Research identifies clear electromagnetic anomalies from a variety of satellite data, potentially aiding the development of early warning systems for earthquakes.
According to a new study in De Gruyter’s Journal of Applied Geodesy, earthquakes may betray their impending presence much earlier than previously thought through a variety of anomalies present in the ground, atmosphere and ionosphere that can be detected using satellites.
Developing early warning systems for earthquakes could be very helpful in preventing death and destruction. One such proposed technique involves using satellites to monitor a variety of physical and chemical parameters within the ground, atmosphere, and the layer of charged particles that exists above it, called the ionosphere.
Challenges in Detecting Earthquake Precursors
Such anomalies are known as earthquake precursors, and although researchers are aware of them, it has been difficult to definitively identify a pattern of so-called red flags that could indicate an impending earthquake. This is because of the complexity of precursor interactions and their variability in different earthquakes and geographical regions. However, with every earthquake that researchers analyze using increasingly sophisticated satellite technology, these patterns are slowly emerging.
Professor Mehdi Akhoondzadeh of the University of Tehran assessed a variety of satellite data from the run-up to and aftermath of two earthquakes that occurred on 6 February 2023 near the border between Turkey and Syria. This included data from the Chinese seismo-electromagnetic satellite, CSES-01, and the Swarm satellite mission which consists of three satellites from the European Space Agency.
Observations of Anomalies Before Earthquakes
Strikingly, he observed anomalies in land surface temperature from the earthquake region as early as 12-19 days before the earthquakes and anomalies in atmospheric parameters between 5-10 days before the earthquakes. These included measurements of water vapor, methane levels, ozone, and carbon monoxide.
When Professor Akhoondzadeh investigated anomalies in the ionosphere, including measurements of parameters such as electron density and electron temperature, he found clear and striking anomalies at 1-5 days before the earthquakes.
The times that the anomalies became apparent in the ground, atmosphere, and ionosphere respectively suggest that these signals originated in the ground and eventually became apparent at higher levels in the atmosphere and finally the ionosphere.
Studying these phenomena could pave the way for earthquake early warning systems, but researchers will need to assess other earthquakes in the future to more fully understand these patterns.
“Using CSES-01 satellite data, anomalies in the ionosphere prior to the earthquakes in Turkey on 6 February 2023 have been detected for the first time,” said Professor Akhoondzadeh. “By studying anomalies associated with multiple earthquake precursors, the uncertainty in detecting real anomalies decreases and this can be effective in creating earthquake warning systems with a low number of false warnings.”
Reference: “Analyses of data from the first Chinese seismo electromagnetic satellite (CSES-01) together with other earthquake precursors associated with the Turkey earthquakes (February 6, 2023)” by Mehdi Akhoondzadeh, 16 May 2024, Journal of Applied Geodesy.
DOI: 10.1515/jag-2024-0024

